
A couple of years earlier, he experienced proximal medial arch pain on the left side and progressive flattening of the arch with severe heel valgus. A standing view from behind shows a patient with long-standing flatfeet and mild heel valgus. (From Kliegman RM, et al: Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 18th ed. Lateral weight-bearing radiograph demonstrating features of flatfoot. (From Noble J, et al: Textbook of Primary Care Medicine, 3rd ed. Unilateral acquired adult flatfoot caused by posterior tibial tendon rupture of left foot. Surgical correction of rigid flatfoot may include excision of a cuneonavicular or a talocalcaneal coalition, osteotomy, or lateral column lengthening.įig. Conservative treatment for rigid flatfoot includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corrective shoe wear, and/or casting. Operative treatment for flexible flatfoot may include soft tissue correction, fusion, and/or osteotomy. Conservative treatment for flexible flatfoot may include stretching, corrective shoe wear, and/or casting. However, if it is painful or if equinus contracture exists, then treatment may be necessary. Flexible flatfoot often does not need to be treated. The goal for flatfoot treatment is to establish optimal soft tissue support and bone alignment. Rigid flatfoot is caused by bone anomalies such as tarsal coalition, congenial vertical talus, or arthritis. Obesity, neuropathy, soft tissue trauma, and bone trauma are possible causes of tibial tendon insufficiency. Adult-acquired flatfoot, or fallen arches, is commonly believed to be caused by posterior tibial tendon insufficiency. Etiology and Pathophysiology:įlexible flatfoot is caused by laxity of the ligaments.
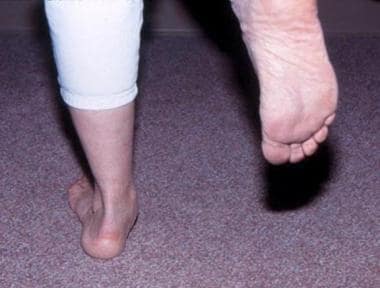
This disorder may be congenital or acquired. Adult-acquired flatfoot is also common however, the exact incidence is unknown because it is often misdiagnosed.

Incidence:įlexible flatfoot is common in young children and may or may not resolve without treatment. In rigid flatfoot, the arch is absent in weight-bearing and non–weight-bearing positions. In flexible flatfoot, the arch is present during non–weight bearing but is lost during weight bearing. It also involves abduction of the forefoot and valgus deformity of the hind foot. Associate Editor, in High Yield Orthopaedics, 2010 Definition:įlatfoot is a condition in which the longitudinal arch of the foot is lost.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
